Collate / Collation
Collations define the sort ordering for things like ORDER BY. Collations also define the casing rules for things like UPPER() and LOWER().
A special collation sequence can be specified for CHAR and VARCHAR field columns; the COLLATE parameter allows fields to be collated according to a certain language/group of languages e.g. collate according to the German language when using Win1252. A full list of collations for database version used, can be found in the system table, RDB$COLLATIONS (the RDB$CHARACTER_SET_ID refers for which character set the collations are for.
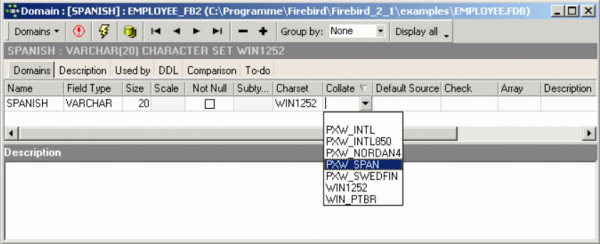
In IBExpert the collation sequence can be specified when defining the character set for a domain or field:
The collation options are offered in IBExpert in a drop-down list, after specifying the character set.
In DDL it is specified using the keyword COLLATE and the respective character set table, for example:
CREATE DOMAIN dom_city VARCHAR(20) COLLATE PXW_INTL850; CREATE DOMAIN User_Name VARCHAR(20) CHARACTER SET DOS437 DEFAULT USER NOT NULL COLLATE PDOX_ASCII
The parameter sequence is important, as the collation sequence must be specified last.
Since Firebird 2.5, there is also a collation option for numerals (only in Unicode collation):
NUMERIC-SORT={0 | 1}
The default, 0, sorts numerals in alphabetical order:
1 10 100 2 20
The parameter, 1, sorts numerals in numerical order:
1 2 10 20 100