Environment Options
Environment Options can be found in the IBExpert Options menu. It enables the user to organize his IBExpert working environment as he wishes. It is possible, for example, to set certain defaults for editors and specific menu items, alter colors or the system font, etc.
Preferences
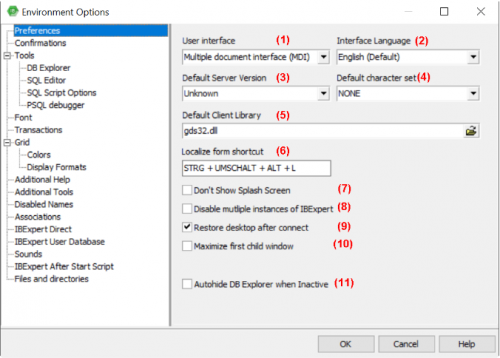
The Preferences window allows the user to specify certain general preferences or defaults.
These include:
(1) User interface
The pull-down list offers the options MDI or SDI.
The user interface is the connection between the machine and the user, i.e. the way the software is presented to the user on-screen. The user interface enables the user to use the program and manipulate data.
Under the IBExpert Options menu item, Environment Options, the user interface can be defined as SDI (Single Document Interface) or MDI (Multiple Document Interface).
When altering the user interface from SDI to MDI and vice versa, IBExpert needs to be restarted for the change to take effect.
(2) Interface language
The default language is English. The pull-down list offers the following alternative languages:
- Czech
- Dutch
- English
- French
- German
- Hungarian
- Italian
- Japanese
- Polish
- Portuguese
- Romanian
- Russian
- Spanish
Should you not be able to see the full list of languages in the drop-down list, either delete the ibexpert.lng file or rename the english.lng file, found in the IBExpert Languages directory, to ibexpert.lng, and place this in the main IBExpert directory.
You can customize or update your language using the IBExpert Tools menu item, Localize IBExpert.
(3) Default server version
If the same database version is used for all projects, it is advisable to set a default version here. This saves having to enter the database server version every time a database is registered. The pull-down list offers the following database versions:
- Unknown (default)
- Firebird 1.0
- Firebird 1.5
- Firebird 2.0
- Firebird 2.1
- Firebird 2.5
- Firebird 3.0
- InterBase 5.x
- InterBase 6.1
- InterBase 6.5
- InterBase 7.0
- InterBase 7.1
- InterBase 7.5
- InterBase 2007
- InterBase 2009
- Yaffil 1.0
(4) Default character set
The default character set is the character set defined when creating the database, and applicable for all areas of the database unless overridden by the domain or field definition. It controls not only the available characters that can be stored and displayed, but also the collation order. If not specified, the parameter defaults to NONE, i.e. values are stored exactly as typed.
Please refer to Default character set for further information.
The following character sets are currently available:
- ASCII
- BIG_5
- CYRL
- DOS437
- DOS850
- DOS852
- DOS857
- DOS860
- DOS861
- DOS863
- DOS865
- EUCJ_0208
- GB_2312
- ISO8859_1
- ISO8859_2
- KSC_5601
- NEXT
- NONE
- OCTETS
- SJIS0208
- UNICODE_FSS
- UTF8
- WINI1250
- WINI1251
- WINI1252
- WINI1253
- WINI1254
(5) Default client library
The GDS32.DLL is dependent upon the database server. Firebird has, in addition to this, its own library, FBCLIENT.DLL. The GDS32.DLL is however also included for compatibility reasons. When working with Firebird, or different Firebird/InterBase® server versions, the DLL can be selected here, as wished; simply click the Open File icon to the right of this field, to select the library required.
As IBExpert is still currently a 32-bit application, it requires a 32-bit client dll. If you try to register a 64-bit Firebird (with the standard 64-bit fbclient.dll) in IBExpert you will get an error message informing you that the fbclient.dll is missing or invalid.
So to use IBExpert with a 64-bit Firebird version, you will need to use the Firebird 32-bit client library. Simply download a 32-bit Firebird version, for example, the fbembed.dll, which is delivered in the full IBExpert installation package and found in the IBEUDB subdirectory.
The Script Executive always uses this default client library unless it is overriden using the SET CLIENTLIB command directly in the Script Executive editor.
(6) Localize form shortcut
Here you can specify your own shortcut for opening the Localizing Form, if you do not wish to use the default [Ctrl + Shift + Alt + L]. The Localizing Form displays all functions and the respective key combinations, which can also be customized. Please refer to Localizing Form for further information.
Check options
The following features can be checked or unchecked as wished:
(7) Don't Show Splash Screen: disables the IBExpert Splash Screen displayed whilst IBExpert is being loaded.
(8) Disable multiple instances of IBExpert: when checked this option ensures that IBExpert is only opened once.
(9) Restore desktop after connect: if this option is checked, IBExpert will restore all those forms left open as the last connection was ended, when it reconnects to the database.
(10) Maximize first child window: the first Editor/window opened is automatically expanded to fill the maximum screen area. This option is only available in the MDI version.
(11) Autohide DB Explorer when inactive: this option hides the DB Explorer automatically, if it is not focused. In other words, when the mouse is held over the left area, the DB Explorer appears; when the mouse is removed to begin work in an editor or child window, the DB Explorer is blended out, offering a larger work area.
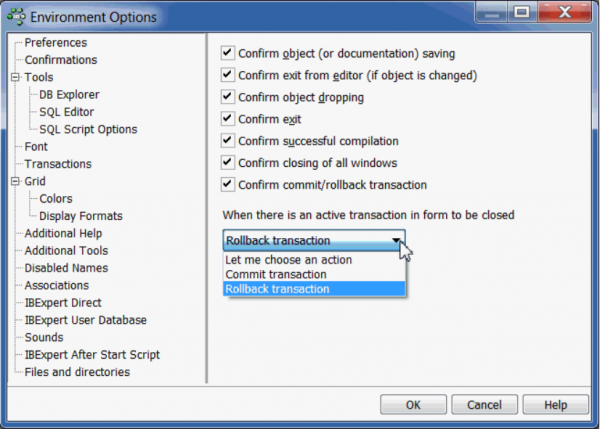
Confirmations
Some users find it annoying to be constantly asked for confirmation, whether or not they really want to carry out an operation. This window allows the user to specify, which confirmations he considers wise.
The following options are available:
- Confirm object (or documentation) saving: if this option is checked, IBExpert will request confirmation before saving object modifications or descriptions.
- Confirm exit from editor (if object is changed): if this option is checked, IBExpert will request confirmation, if alterations have been made, before exiting from an object editor.
- Confirm object dropping (recommended): if this option is checked, IBExpert will request confirmation before dropping any database object.
- Confirm exit: if this option is checked, IBExpert will request confirmation before closing IBExpert.
- Confirm successful compilation: (recommended) if this option is checked, IBExpert displays a dialog, showing whether compilation was successful or not.
- Confirm closing of all windows
- Confirm commit/rollback transaction: (recommended) this option determines whether a message box appears, asking for confirmation when a user commits or rolls back active transactions in the SQL Editor, Table Editor, View Editor or Stored Procedure Editor.
- When there is an active transaction in form to be closed: this option allows you to control which default action should be taken when closing an active transaction. By default IBExpert asks for your choice for each active transaction when you close a form. Now you can select from the options Let me choose an action, Commit or Rollback.
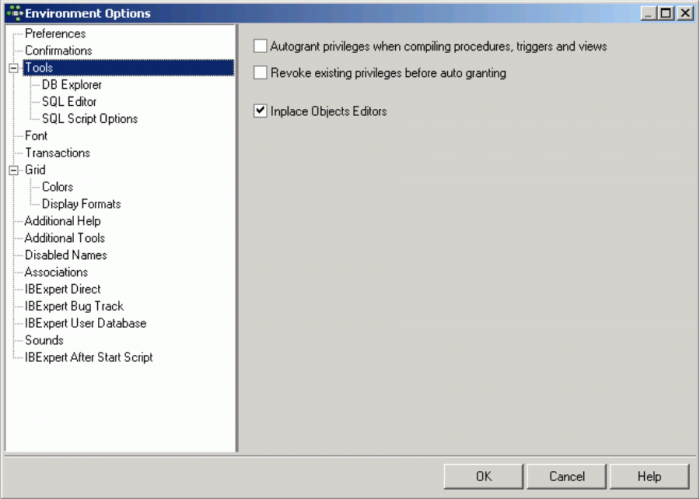
Tools
The Tools page allows the user to specify the following for all tools if wished:
- Autogrant privileges when compiling procedures, triggers and views: this saves the repetitive task of autogranting privileges on the Grants page of the object editors each time a new procedure, trigger, view, packages and functions is created, and prevents the problems which inevitably arise should the assignment of rights be forgotten.
- Revoke existing privileges: if this option is enabled, an object's (stored procedure, trigger, view) existing privileges will be deleted before granting it new privileges.
- Inplace Objects Editors: this item applies to the so-called editors within editors.
For example, the Table Editor is active and a trigger is selected on the Trigger page: if this option is not checked, an SQL Editor window appears automatically in the lower part of the Table Editor, displaying the trigger code, but not allowing any changes to be made. When this option is however checked, a simple click on a trigger automatically opens the Trigger Editor in this lower area, enabling work to be done on it, without having to leave the Table Editor and opening the Trigger Editor.
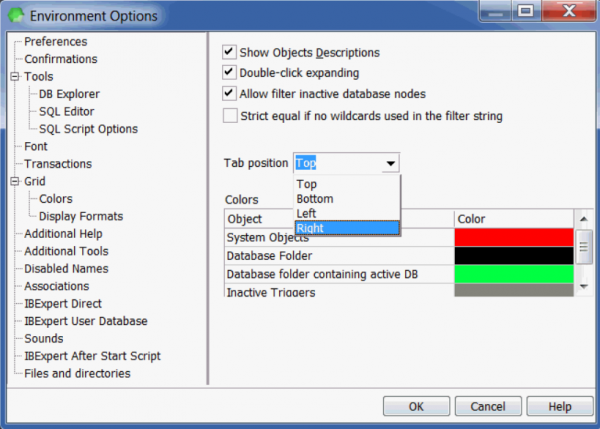
DB Explorer
Here it is possible to specify whether database object descriptions should be displayed or not (this only makes sense if object descriptions are entered by the user), and whether double-click expanding (for the DB Explorer tree) is desired. Further options include a check-box option to allow filtering of inactive database nodes and a drop-down list for the specification of the tab position of the Database Explorer pages.
Furthermore, colors may be specified for the following:
- system objects
- database folders
- database folder containing active DB
- inactive triggers
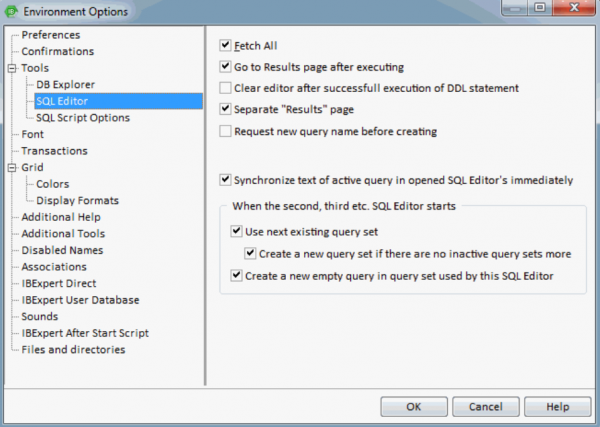
SQL Editor
The following options may be user-defined for the SQL Editor:
- Go to Results page after executing: this option is only worth checking of course if you have specified Separate Results page (see below).
- Clear editor after successful execution of DDL statement: this clears the results page after the query has been committed.
- Separate Results page: turn this option off to place SQL query results directly below the code editor, or activate it to display query results on a separate page (found directly to the right of the Edit page).
- Request new query name immediately before creating: If this option in enabled IBExpert will request a new query name just before creating it.
The following set of options control the behavior of the SQL Editor's Query Manager, when multiple instances of the SQL Editor are started:
- Synchronize text of active query in opened SQL Editors immediately when the second, third etc. SQL Editor starts
- Use next existing query set
- Create a new query set when there are no more inactive query sets
- Create a new empty query in query set used by this SQL Editor
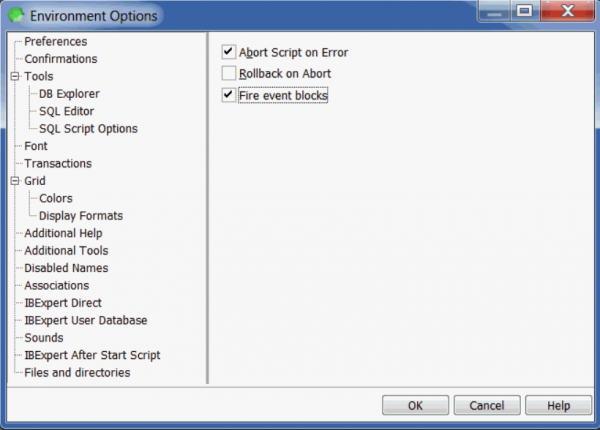
SQL Script Options
The SQL Script Options page offers the following user specifications:
- Abort Script on Error: the script execution is halted the moment an error is detected.
- Rollback on Abort: the script is automatically rolled back the moment an error is detected in the script. This option is only possible, if the first item, Abort Script on Error, is already selected.
- Fire event blocks: please refer to the Script Executive's Options page for further information.
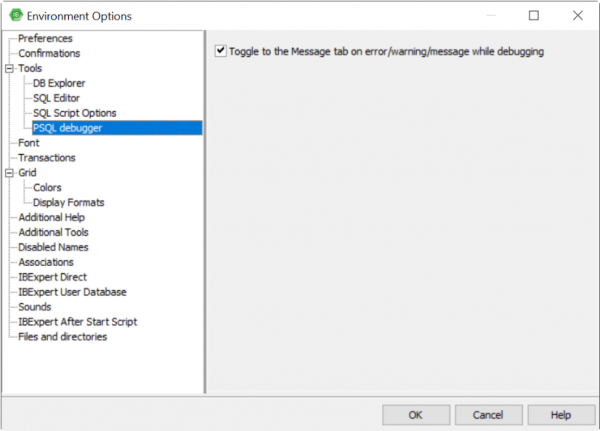
PSQL Debugger
- Toggle to the Message tab on error/warning/message while debugging: By default the PSQL Debugger activates the Message tab on every error/warning/message occurred while debugging. If you don't like the default behaviour turn this option off.
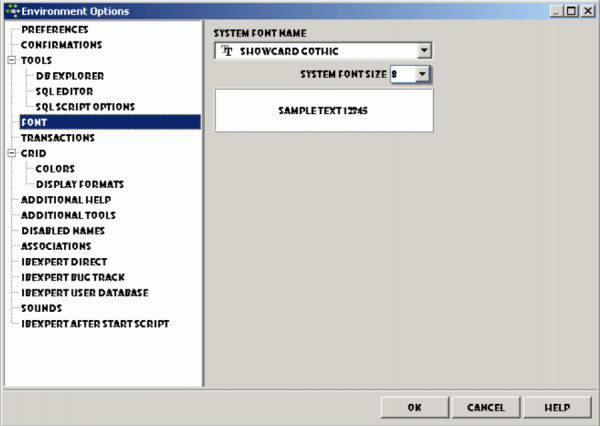
Font
Here it is possible for the user to specify the system (i.e. IBExpert) font name and size. The Sample Text 12345 displays the specified font as it will appear in IBExpert.
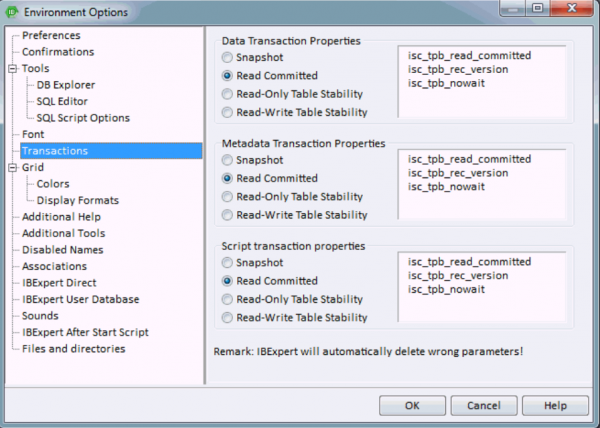
Transactions
Here certain additional data, metadata and script default transaction properties may be defined for the server connection.
These are all Firebird/InterBase® API terms, and may be checked as wished.
Data Transaction Properties:
- Snapshot
- Read Committed
- Read-Only Table Stability
- Read-Write Table Stability
Metadata Transaction Properties:
- Snapshot
- Read Committed
- Read-Only Table Stability
- Read-Write Table Stability
Script Transaction Properties:
- Snapshot
- Read Committed
- Read-Only Table Stability
- Read-Write Table Stability
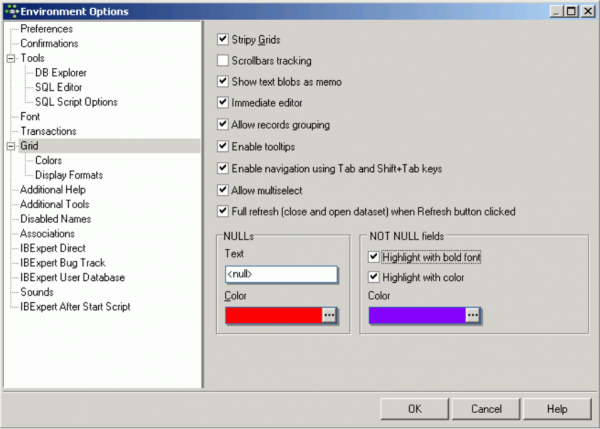
Grid
Here a range of options are available, applicable for all data grids:
Check boxes for the following options:
- Stripy Grids: makes reading wide lines of data rows easier.
- Scrollbars tracking
- Show text blobs as memo: The memo option enables the blob to be easily read by simply focusing the cursor over the blob field.
- Immediate editor: Enables immediate editing in the data grid by simply placing the cursor on a field, as opposed to having to first double-click on the field, in order to edit it.
- Allow records grouping: When this option is checked, an additional gray bar appears above the column headers over the grid. A column header simply needs to be dragged 'n' dropped into this area, to group by the selected column. A reorganized data view appears, where the group contents can be revealed or hidden, by clicking on the '+' or '-' buttons. Please note that this is not the same as the data grid right-click menu item Group Fields/Ungroup Fields.
- Enable tooltips: when checked, this option displays the full field contents when the cursor is held over a particular field, if the column width is not sufficient to display all information. This is useful, if tables with many columns and long field contents need to be scanned.
- Enable navigation using [Tab] and [Shift + Tab] keys
- Allow multiselect: allows multiple data sets to be selected for editing (e.g. copying). If this is not checked, it is only possible to select one data set at a time. The change of mode can be recognized by the form/shade of the arrow on the left when pointing at a selected data set.
- Full refresh (close and open dataset) when Refresh button clicked: by default, the Refresh button in all IBExpert Data grids refreshes only the current record, not the entire record set. if you wish to use the data grids to enter multiple data sets, you can alter this default value by checking this option.
Furthermore, it is possible to specify the exact representation of a NULL and NOT NULL fields. The default value is displayed as <null> (in red). NOT NULL fields can be displayed as bold text or be highlighted with color.
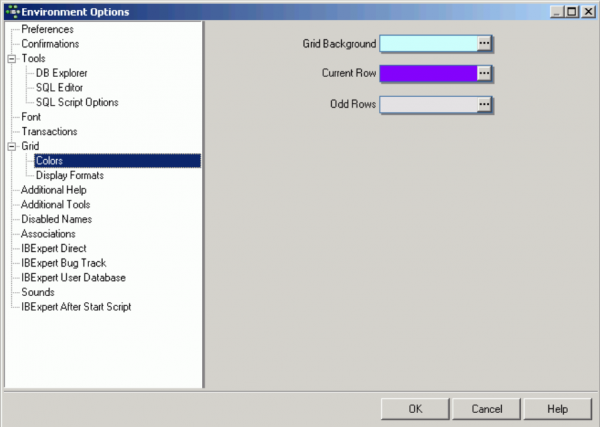
Colors
Here the user can specify the colors for different elements in the grids:
- Grid Background
- Current Row
- Odd Rows
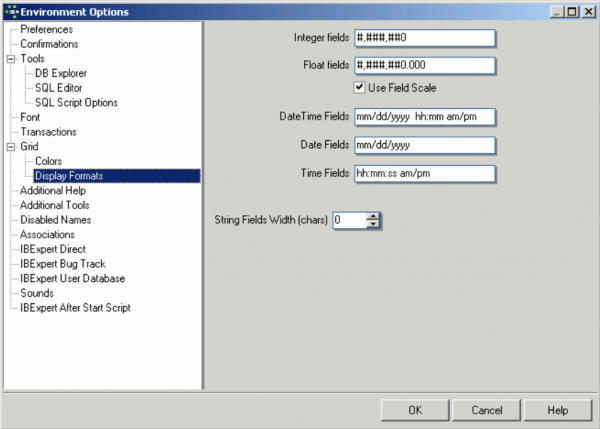
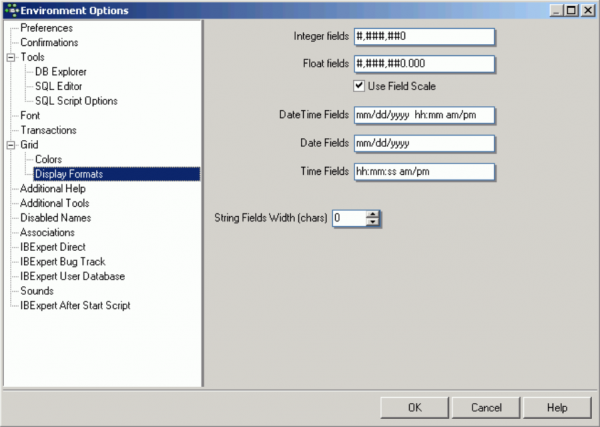
Display Formats
These options allow the user to specify the display format in grids for INTEGER, FLOAT, DATE, TIME and DATE/TIME fields.
Further options include a check box option for Use field scale, which allows a field definition to override these standard specifications, and an option to specify the String fields' width for characters.
The following lists the various date and time formatting options available.
Date Time Formats
The following format allows you to alter the way the date and time is displayed. Please note that this does not alter the way this information is stored, only the way it is displayed.
Date time format strings specify the formatting of date-time values (such as TDateTime) when they are converted to strings. Date time format strings are passed to formatting methods and procedures (such as FormatDateTime), and are also used to set certain global variables (such as ShortDateFormat).
They are composed from specifiers that represent values to be inserted into the formatted string. Some specifiers (such as d), simply format numbers or strings. Other specifiers (such as /) refer to local-specific strings from global variables.
In the following table specifiers are given in lower case. Case is ignored in formats, except for the am/pm and a/p specifiers.
Specifier Displays
| c | Displays the date using the format given by the ShortDateFormat global variable, followed by the time using the format given by the LongTimeFormat global variable. The time is not displayed if the date-time value indicates midnight precisely. |
| d | Displays the day as a number without a leading zero (1-31). |
| dd | Displays the day as a number with a leading zero (01-31). |
| ddd | Displays the day as an abbreviation (Sun-Sat) using the strings given by the ShortDayNames global variable. |
| dddd | Displays the day as a full name (Sunday-Saturday) using the strings given by the LongDayNames global variable. |
| ddddd | Displays the date using the format given by the ShortDateFormat global variable. |
| dddddd | Displays the date using the format given by the LongDateFormat global variable. |
| e | Displays the year in the current period/era as a number without a leading zero (Japanese, Korean and Taiwanese locales only). |
| ee | Displays the year in the current period/era as a number with a leading zero (Japanese, Korean and Taiwanese locales only). |
| g | Displays the period/era as an abbreviation (Japanese and Taiwanese locales only). |
| gg | Displays the period/era as a full name. (Japanese and Taiwanese locales only). |
| m | Displays the month as a number without a leading zero (1-12). If the m specifier immediately follows an h or hh specifier, the minute rather than the month is displayed. |
| mm | Displays the month as a number with a leading zero (01-12). If the mm specifier immediately follows an h or hh specifier, the minute rather than the month is displayed. |
| mmm | Displays the month as an abbreviation (Jan-Dec) using the strings given by the ShortMonthNames global variable. |
| mmmm | Displays the month as a full name (January-December) using the strings given by the LongMonthNames global variable. |
| yy | Displays the year as a two-digit number (00-99). |
| yyyy | Displays the year as a four-digit number (0000-9999). |
| h | Displays the hour without a leading zero (0-23). |
| hh | Displays the hour with a leading zero (00-23). |
| n | Displays the minute without a leading zero (0-59). |
| nn | Displays the minute with a leading zero (00-59). |
| s | Displays the second without a leading zero (0-59). |
| ss | Displays the second with a leading zero (00-59). |
| z | Displays the millisecond without a leading zero (0-999). |
| zzz | Displays the millisecond with a leading zero (000-999). |
| t | Displays the time using the format given by the ShortTimeFormat global variable. |
| tt | Displays the time using the format given by the LongTimeFormat global variable. |
| am/pm | Uses the 12-hour clock for the preceding h or hh specifier, and displays am for any hour before noon, and pm for any hour after noon. The am/pm specifier can use lower, upper, or mixed case, and the result is displayed accordingly. |
| a/p | Uses the 12-hour clock for the preceding h or hh specifier, and displays a for any hour before noon, and p for any hour after noon. The a/p specifier can use lower, upper, or mixed case, and the result is displayed accordingly. |
| ampm | Uses the 12-hour clock for the preceding h or hh specifier, and displays the contents of the TimeAMString global variable for any hour before noon, and the contents of the TimePMString global variable for any hour after noon. |
| / | Displays the date separator character given by the DateSeparator global variable. |
| : | Displays the time separator character given by the TimeSeparator global variable. |
| 'xx'/“xx” | Characters enclosed in single or double quotes are displayed as-is, and do not affect formatting. |
Example
To format the date as month, day, year and the time as am or pm, simply enter the following on the Display Formats page:
Simply alter DateTime Fields to: mm/dd/yyyy hh:mm am/pm: and Time Fields to hh:mm:ss am/pm
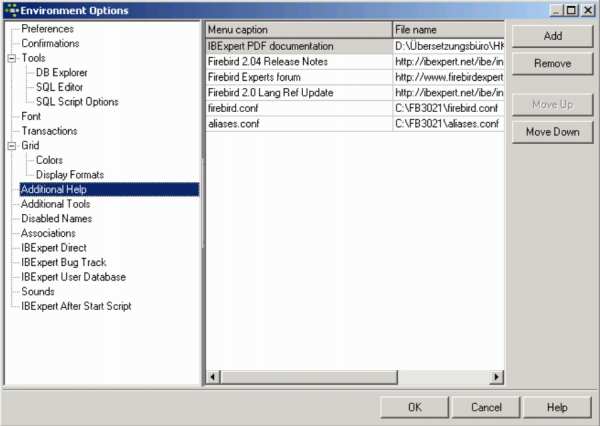
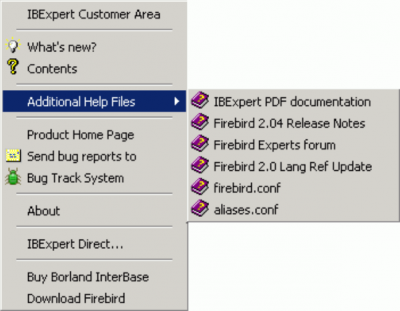
Additional Help
The Additional Help window allows the user to add certain additional help files. This is particularly useful for incorporating the help files of third party components, installed in the IBExpert PlugIns menu or the IBExpert Tools menu item, External Tools.
An additional menu item is automatically inserted in the IBExpert Help menu, for each of these help files.
See also:
Additional Tools
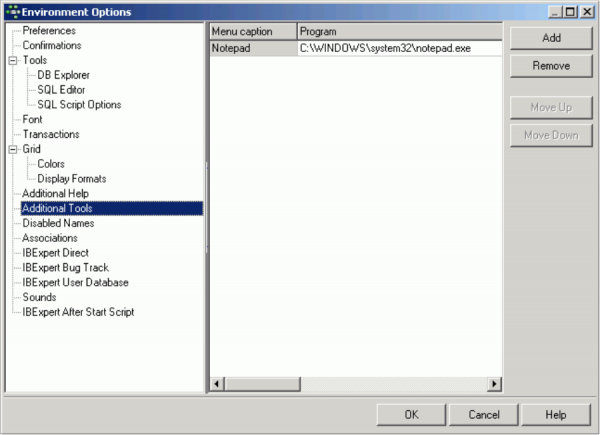
The Additional Tools dialog allows the user to add certain additional third party tools. Once additional tools have been uploaded here, an extra menu item, External Tools, appears in the IBExpert Tools menu, allowing the user to quickly open his third party tools directly from IBExpert.
Disabled Names
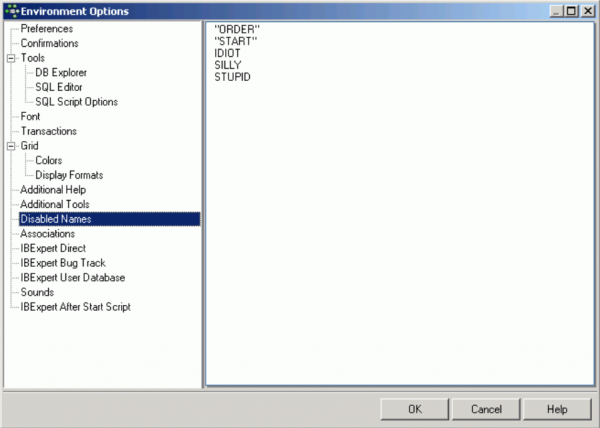
This page can be used to define a list of disabled object names.
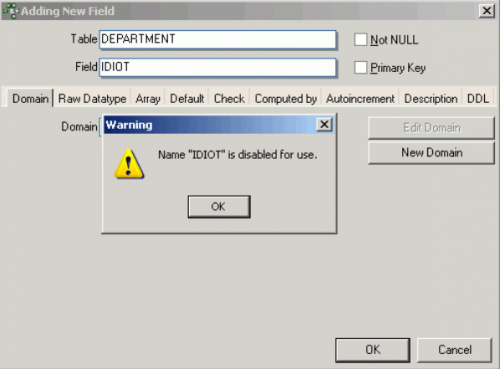
IBExpert refers to this list, when new database objects (and fields) are created, and publishes a warning if the new name corresponds to any name in this list.
Names that should be avoided because they are Firebird keywords, such as ORDER and START (Firebird 2.1) do not need to be added to this list, as they are automatically generated by IBExpert with the necessary quotation marks (“). If you wish to avoid metadata names in quotation marks, these words need to be typed with the quotation marks in the list of disabled names (see illustration above).
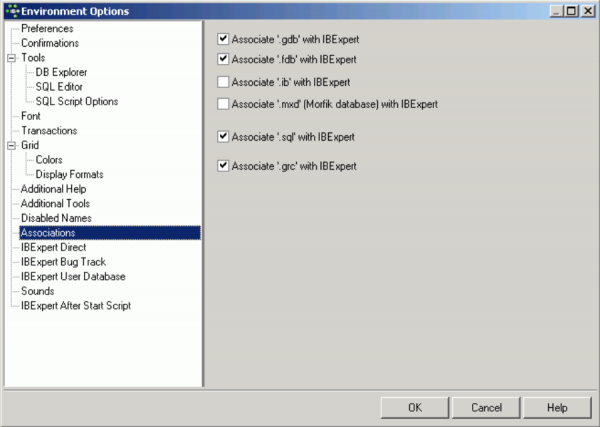
Associations
This dialog is important, to specify which file types IBExpert should recognize and associate with the Firebird/InterBase® database. The check list includes the following suffixes:
- .GDB
- .FDB
- .IB
- .SQL
- .GRC
IBExpert Direct
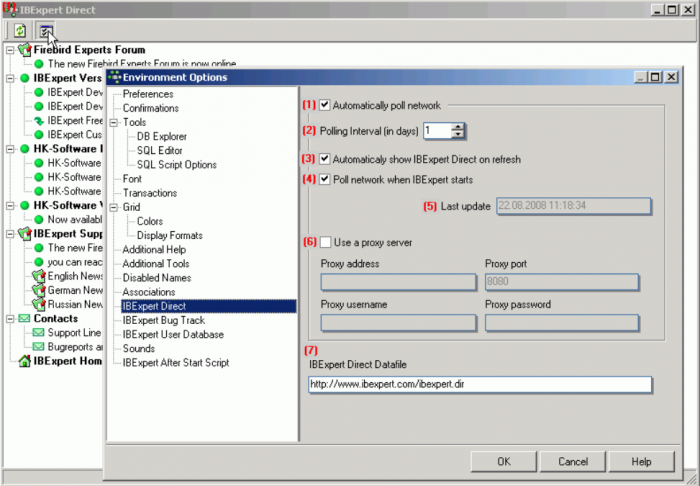
The IBExpert Direct dialog allows the user to specify a number of options concerning this IBExpert menu item found in the Help menu. The IBExpert configuration window can be started either from the IBExpert Options menu item, Environment Options or alternatively directly from the IBExpert Help menu item, IBExpert Direct, using the respective icon:
The options available include the following:
(1) Automatically poll network: this is recommended, as IBExpert Direct is an important information source, informing all users of news concerning IBExpert, such as new versions, documentation, downloads, plugins, forums, as well as contact addresses and a direct link to the IBExpert home page, https://ibexpert.net/ibe/.
(2) The polling interval in days can be user-specified. Check boxes allow the user to specify whether IBExpert Direct should (3) automatically shown on refresh, or whether (4) the network should be polled for new items, each time IBExpert is started.
(5) The Last update field is purely a display field, showing the last time the network was polled for new IBExpert Direct news items.
(6) It is also possible to specify a proxy server if necessary, with fields for specification of the proxy address, port, user name and password.
(7) The last field displays the IBExpert Direct link address for IBExpert to internally download the file.
IBExpert User Database
The complete IBExpert configuration and work is stored in the IBExpert User Database. The user database should always be used for your main storage for security reasons. It is also possible to store SQL scripts in the IBExpert User Database. These scripts can then be viewed and opened using the Scripts/Blocks page in the DB Explorer.
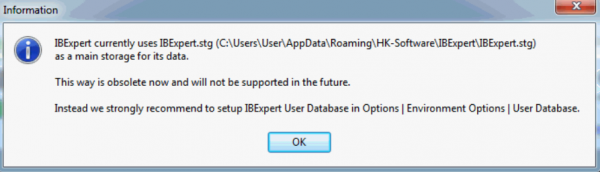
If you have not specified and registered your IBExpert User database, you will receive the following error message, the first time you start IBExpert:
By starting IBExpert for a second time, IBExpert automatically creates a User Database in the user\app directory.
If you do not specify the name and location of the IBExpert user database yourself, the default ibexpert.udb will be used for storage of all settings, which can be found here: \HK-Software\IBExpert\ibexpert.udb. Please note, this area is user-dependent and even if several users work on one machine, each user has their own file.
You can of course specify the location of the User Database yourself. The simplest and quickest way to do this is using the supplied Firebird embedded server.
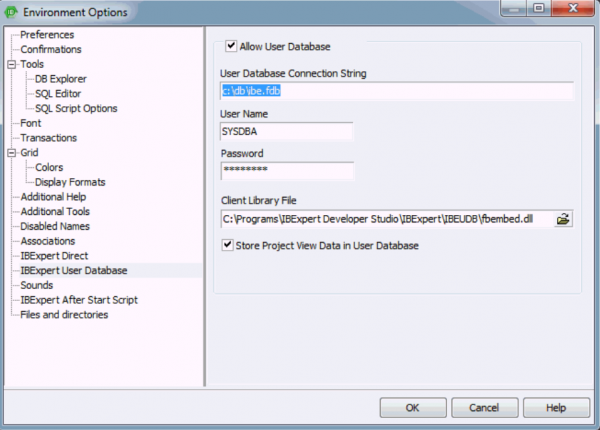
Use the Environment Options menu item, User Database:
The following information is required in order to create a new user database. After checking the Allow User Database checkbox the following fields need to be completed:
- User Database Connection String: Use this field to specify a local file path, e.g. c:\db\ibe.fdb. Important: do not quote a server name if you are intending to use the recommended local Embedded Server.
- User Name (default: SYSDBA).
- Password (masterkey).
- Client Library File here you should select the fbembed.dll located in the IBExpert \IBEUDB subdirectory. As IBExpert is still currently a 32-bit application, it requires a 32-bit client dll. If you try to register a 64-bit Firebird (with the standard 64-bit fbclient.dll) in IBExpert you will get an error message informing you that the fbclient.dll is missing or invalid. So to use IBExpert with a 64-bit Firebird version, you will need to use the Firebird 32-bit client library.
- Check box: Store Project View Data in User Database.
If you do not specify the location for your user database here, the default location \HK-Software\IBExpert\ibexpert.udb will be used. This location is however user-dependent. We recommend that you specify a non-user-dependent directory and path for your user database using this menu function. If you need to - either to another user on the same machine, or another machine, you simply specify the directory and path here, or copy the IBExpert.udb to the new machine.
Since IBExpert version 2020.05.10 it is possible to use environment variables in a database path and client library. To use the value of an environment variable as a part of a path enclose it between the percent chars (%):
\somedata\ibedb.fdb
There is an IBE_APPDIR environment variable that contains the location of the IBExpert.exe directory.
The user database can then be created and initialized using the Create and Init User Database button, and then registered using the IBExpert Database menu item, Register Database. From now on you should no longer see the error message when starting IBExpert.
You can also set the User Database properties from an INI-file.
If you wish to store the IBExpert User Database on a network drive, we recommend the following procedure: move the client library file, fbembed.dll, from the IBExpert subdirectory, \IBEUDB to a location of your own choice (but without the localhost: prefix), and rename the database with a valid name of your choice. The User Database then uses Firebird's Embedded Server.
Please also refer to the IBEBlock article: Performing a daily backup of the IBExpert User Database.
Detecting and moving your user database
We are often asked, how all IBExpert settings, such as database registrations, can be ported when installing IBExpert on another computer.
If you have specified the location and name of your user database in Environment Options / User Database, you can move it from here to the new location.
If you have not specified a location yourself: by default, the user database file can always be found in the folder: \HK-Software\IBExpert\ibexpert.udb. This area is user-dependent and even if several users work on one machine, each user has their own file.
Search for the file ibexpert.udb on your computer. If it is found, either copy it to the path mentioned above or create a user-independent path, e.g. c:\db\ibexpert.udb.
Restart IBExpert and enter the selected path into the User Database and restart again. Following this process all entries from the previous User Database should be visible again.
Setting User Database properties from an INI-file
IBExpert looks for IBExpert.ini file in the current directory. If there is no IBExpert.ini file in this directory - the user profile directory will be searched too.
If the IBExpert.ini file is found, IBExpert will read the “UserDB” section, if it exists. Four parameters are possible in this section:
- UDBConnectString - the User Database connection string;
- UDBUserName - user name
- UDBPassword – password
- UDBClientLib - path to client library file (fbclient.dll if omitted)
Only the UDBConnectString parameter is mandatory. If this parameter is found IBExpert will connect to the specified database instead of getting the User Database connection properties from the Windows Registry.
Example of the IBExpert.ini file:
[UserDB] UDBConnectString=USERDB.FDB UDBUserName=SYSDBA UDBPassword=masterkey UDBClientLib=..\Firebird\fbembed.dll
ibexpert.stg
Please note that since version 2011.12.01 IBExpert uses the Firebird database and Firebird Embedded 2.5 to store IBExpert data (registered databases, query histories etc.) by default. In previous versions by default IBExpert stored this data in the IBExpert.stg file and the user was able to change this manually in the User Database. Working with IBExpert.stg is still possible (for example, if you disable the User Database manually) but you will get a warning every time you start IBExpert (refer to image at top of page), and we will not support this method in the future.
Pre-2011.12.01: If you wish to copy the specifications for a database already registered in one IBExpert version over to another IBExpert version, simply copy the file: \Documents and Settings\<user>\Application Data\HK-Software\IBExpert\IBExpert.stg. The preferable solution is however to change to the IBExpert User Database.
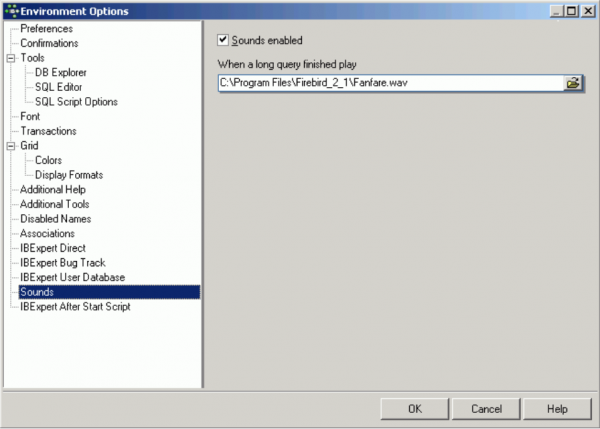
Sounds
Using the Sounds preference, it is possible to specify a .WAV file to announce the end of a time-consuming query.
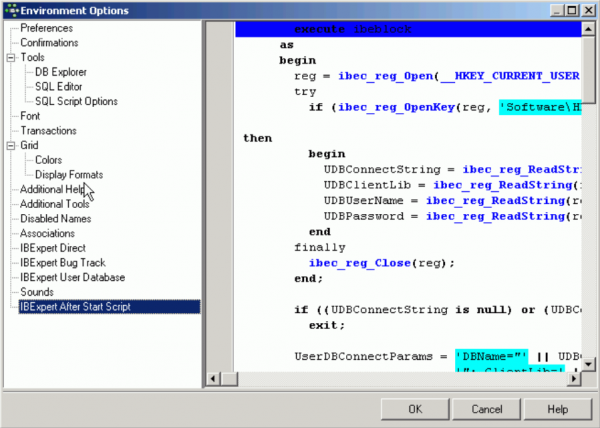
IBExpert After Start Script
Examples
The following example illustrates how to use the After Start Script to find all database registration records with missing database files (if local access is used), and place them into an individual folder. This only works with the User Database.
execute ibeblock
as
begin
reg = ibec_reg_Open(__HKEY_CURRENT_USER, 0);
try
if (ibec_reg_OpenKey(reg, 'Software\HK Software\IBExpert\CurrentData', FALSE))
then
begin
UDBConnectString = ibec_reg_ReadString(reg, 'UDBConnectString');
UDBClientLib = ibec_reg_ReadString(reg, 'UDBClientLib');
UDBUserName = ibec_reg_ReadString(reg, 'UDBUserName');
UDBPassword = ibec_reg_ReadString(reg, 'UDBPassword');
end
finally
ibec_reg_Close(reg);
end;
if ((UDBConnectString is null) or (UDBConnectString = '')) then
exit;
UserDBConnectParams = 'DBName="' || UDBConnectString ||
'"; ClientLib=' || UDBClientLib ||
'; User=' || UDBUserName ||
'; Password=' || UDBPassword ||
'; Names=UNICODE_FSS; SqlDialect=1';
UserDB = ibec_CreateConnection(__ctInterBase, UserDBConnectParams);
try
ibec_UseConnection(UserDB);
-- Looking for missing database files (for local databases only)
MissingFiles = null;
i = 0;
PropIni = ibec_ini_Open('');
try
for select id, props from databases
where (rec_type = 0) and (props containing 'Protocol=3')
into :id, :props
do
begin
Props = '[DB]' || ibec_CRLF() || Props;
ibec_ini_SetStrings(PropIni, Props);
Props = ibec_ini_GetStrings(PropIni);
DBFile = ibec_ini_ReadString(PropIni, 'DB', 'DBNames', '');
if ((DBFile <> '') and (not ibec_FileExists(DBFile))) then
begin
MissingFiles[i] = ID;
i = i + 1;
end;
end;
finally
ibec_ini_Close(PropIni);
end;
if (i > 0) then
begin
ParentID = null;
select id from databases
where (rec_type = 1) and (props containing 'FolderCaption=***MISSING DATABASE FILES***')
into ParentID;
if (ParentID is null) then
begin
ParentID = gen_id(GEN_DATABASE_ID, 1);
insert into databases (ID, PARENT_ID, REC_TYPE, DB_ORDER, PROPS)
values (:ParentID, 0, 1, 0, 'FolderCaption=***MISSING DATABASE FILES***');
commit;
end
for i = 0 to ibec_High(MissingFiles) do
begin
id = MissingFiles[i];
update databases set parent_id = :ParentID where id = :id;
commit;
end
end;
finally
ibec_CloseConnection(UserDB);
end;
end
The following example shows how you can limit access for certain named users to certain IBExpert features, using a combination of an IBEBlock script and an an After start script:
execute ibeblock
as
begin
pwd='';
if (ibec_InputQuery('Start','Please enter password',pwd))
then
if (pwd='123') then
ibec_enablefeature(0);
else
ibec_disablefeature(0);
end
Please also refer to the IBEBlock example, Disable and enable IBExpert features.